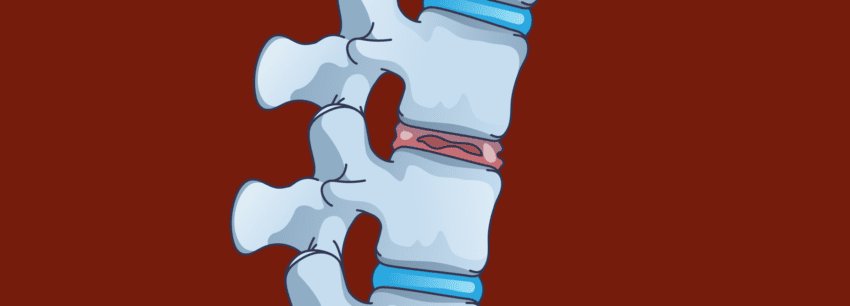
The spine is your body’s most valuable player (MVP), providing structural support, protection of vital organs, and the ability to move throughout your entire life. Composed of vertebrae (bones) and discs, the spine remarkably keeps you both strong and flexible. Discs are gel-like cushions between each vertebra and act as shock absorbers by distributing weight and external forces, allowing for flexibility and movement. Each disc has a firm outer layer called the annulus and a softer inner core called the nucleus. Together, they contribute to the flexibility and strength needed to support the spine.
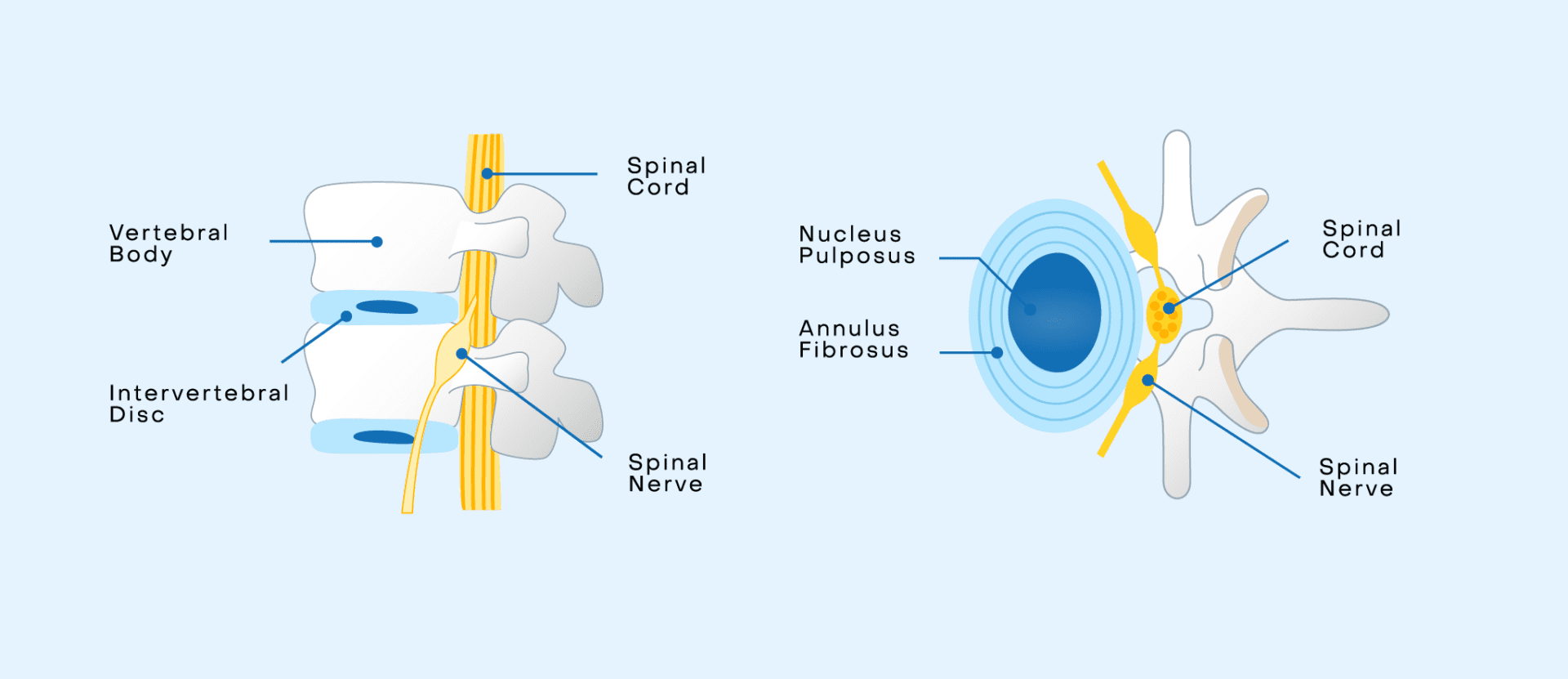
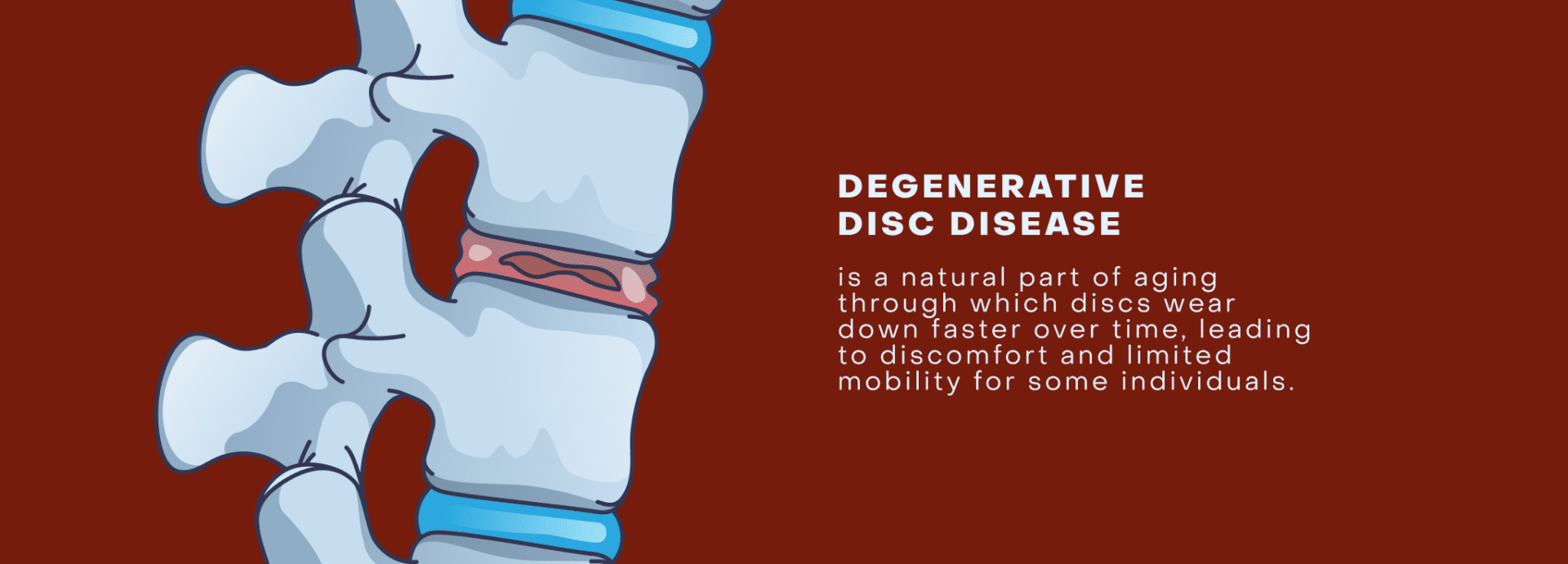
But like any hardworking MVP, our discs undergo natural wear and tear over time, known as degeneration. As they lose water content, lose height, become less flexible, and develop small cracks or tears, this natural process can sometimes lead to symptoms. Symptomatic degeneration of the discs is a condition with a big name and an even bigger reputation: Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD).
What Is Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD)?
Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD) is a condition where the discs of the spine break down, causing pain and other problems in the spine. This condition commonly affects the cervical (neck) and lumbar (low back) regions of the spine because these regions move quite a bit, resulting in greater wear. The thoracic (mid back) region experiences less motion and wear in comparison because this region of the spine is stabilized by the rib cage.
While DDD sounds like a serious condition, it’s often misunderstood. For starters, DDD isn’t actually a disease, but rather is a condition, characterized by discomfort and dysfunction associated with disc degeneration. Common symptoms include low back or neck pain and can worsen with prolonged positions like sitting or standing, bending forward, or lifting heavy objects.
Significant factors such as age, genetics, lifestyle, and previous injuries all contribute to the development of disc degeneration and can cumulatively increase the risk for symptoms. Furthermore, people who engage in repetitive strain activities, like high-intensity sports or physically demanding jobs, or who have had spine injuries, may be more susceptible. However, anyone can experience symptoms related to disc degeneration.
One of the most common misconceptions is that all disc degeneration is painful or requires treatment. Many people experience disc degeneration without any noticeable symptoms. In fact, signs of disc degeneration are common MRI findings in adults (estimated as 90% of adults over the age of 60 years), but many will have no symptoms or limitations related to the incidental MRI findings. Also, there are those experiencing symptoms like pain and reduced mobility but do not show significant MRI abnormalities.
What are the common symptoms of Degenerative Disc Disease?
- Low back (or neck) pain: Symptoms may include dull, constant ache, sharp, stabbing pain, or burning or tingling sensation.
- Low back pain with prolonged sitting and standing: This can put a strain on your lower spine, increase pressure inside the discs, and lead to discomfort and stiffness.
- Low back pain with bending forward and heavy lifting: Everyday movements like lifting heavy objects and bending forward to pick up something can overstress the discs of the lumbar spine.
- Neck pain with bending the neck forward: The widespread overuse of smartphones leads to issues like “tech neck,” “text neck,” or iPosture. “Tech neck” strains and damages the neck due to frequently looking down at phones, tablets, or other devices for extended periods. Certain occupations or activities also require this extended neck position.
What are the factors that contribute to Degenerative Disc Disease?
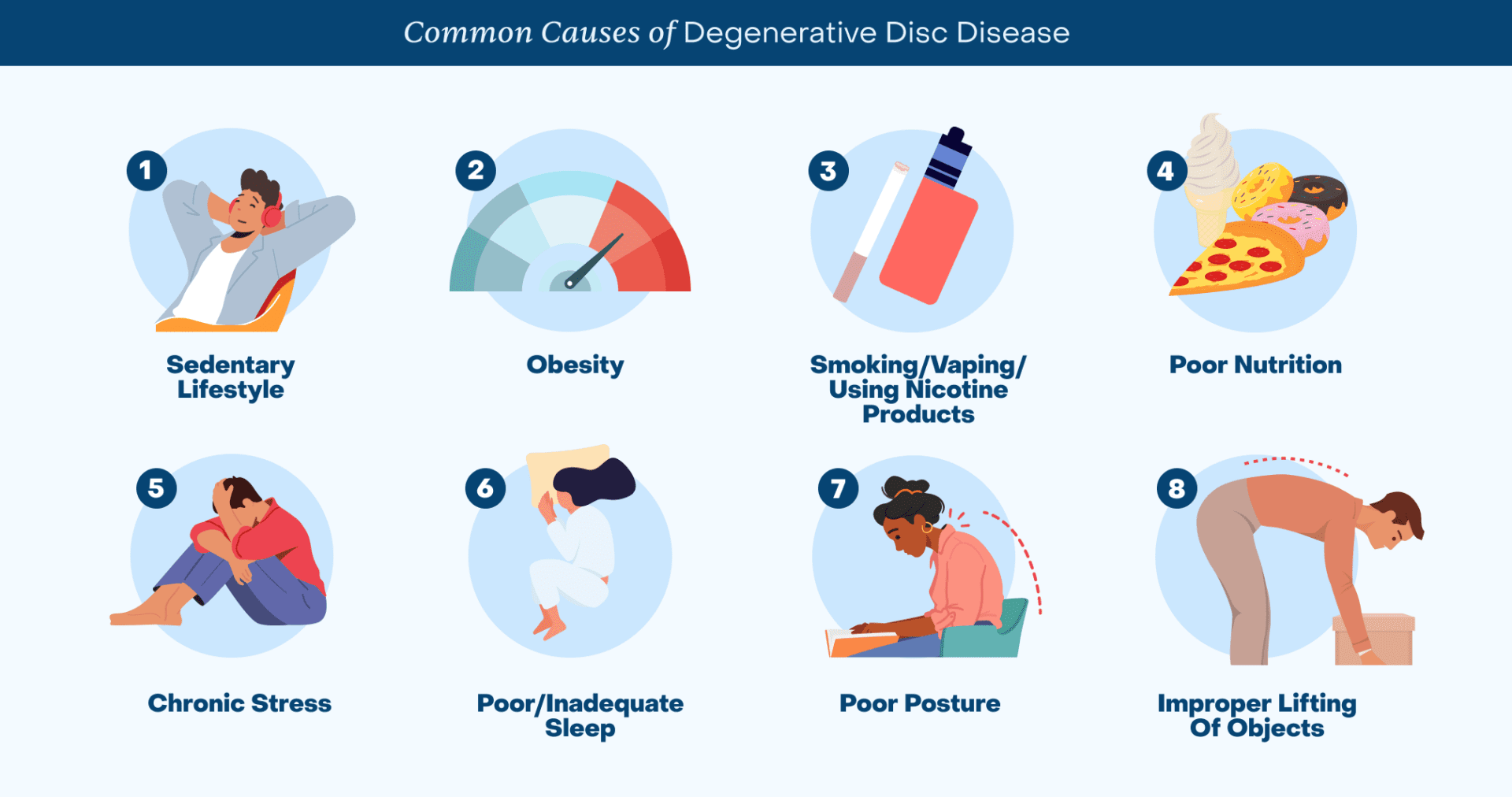
Several daily habits are important to consider because they can accelerate DDD and/or increase the risk of symptoms caused by DDD:
- Improper lifting of objects
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Obesity
- Smoking/Vaping/Using Nicotine products
- Poor nutrition
- Chronic stress
- Poor/Inadequate sleep
- Poor posture
- Improper lifting of objects
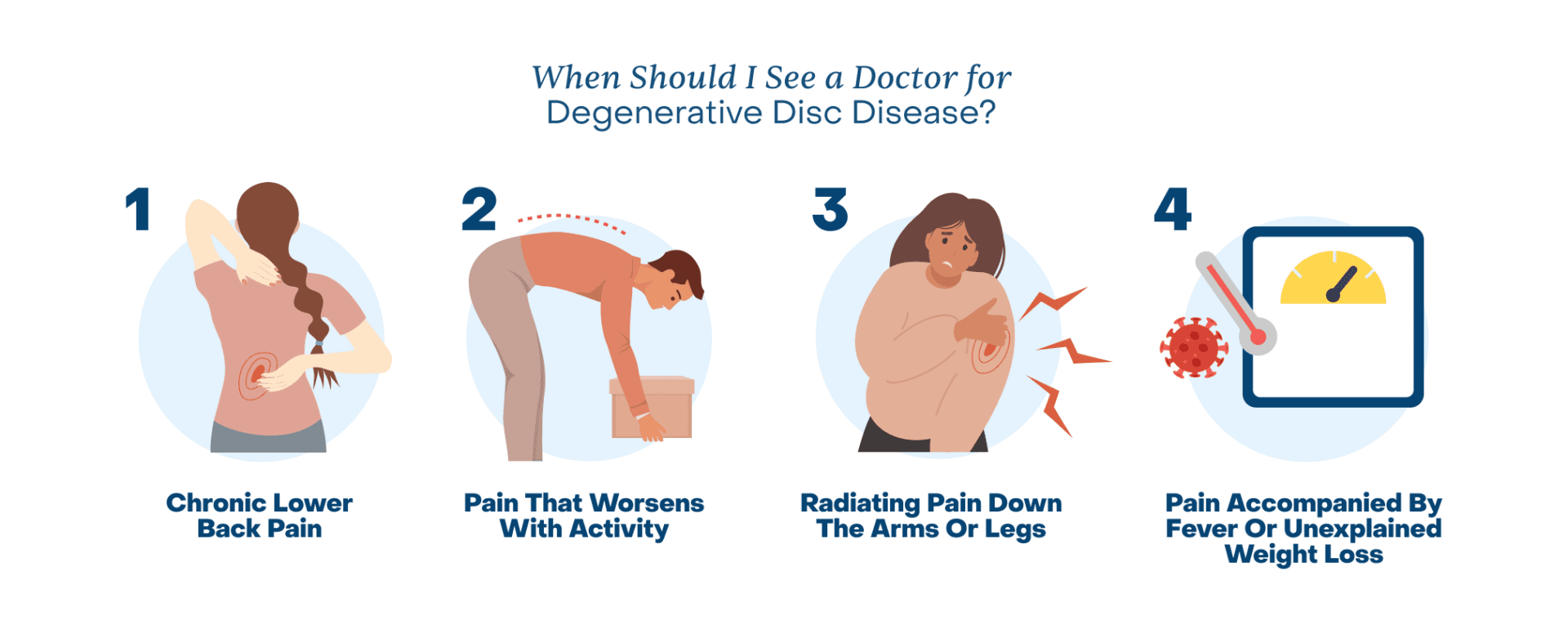
When Should I See a Doctor for Degenerative Disc Disease?
Most back pain improves over time with rest, proper posture, and self-care. However, it’s essential to see a doctor if you experience these common symptoms:
- Chronic Lower Back (or Neck) Pain: Persistent pain that lasts for weeks or months can range from a dull ache to a sharp or burning sensation, leading to reduced range of motion and mobility over time.
- Pain That Worsens with Activity: Sitting for long periods, lifting heavy objects, or even prolonged standing can strain the spine, exacerbating discomfort and preventing participation in routine daily activities.
- Radiating Pain Down the Arms or Legs: Also known as radiculopathy, this pain can feel like a shooting sensation, tingling, or numbness, often caused by nerve compression or irritation in the spine.
- Pain Accompanied by Fever or Unexplained Weight Loss: These symptoms can signal a more serious health issue, such as a spinal infection or tumor, as fever can suggest inflammation or infection, and unexplained weight loss could mean an underlying condition requiring immediate medical attention.
What to Ask Your Doctor about Degenerative Disc Disease
When visiting the doctor, knowing the right questions to ask can help ensure you get the information you need to make informed decisions about your health. Use these questions as a guide at your next appointment:
- What is causing my pain?
- What treatment options are available?
- Are there any lifestyle modifications that can help?
- How long will it take to recover, and when should I return if I’m not improving?
- What are the risks and benefits of surgery, if it is indicated?
- How can I prevent further injury?”

How Can You Manage Degenerative Disc Disease?
DDD can often be managed with lifestyle changes and non-surgical treatments. By staying active, strengthening the muscles around your spine, and practicing proper body mechanics, you can protect your discs and provide much-needed support to minimize symptoms.
Core-strengthening exercises like planks, bridges, bird dogs, and deadlifts can protect the discs. Strengthening the entire core, including muscles of the abdomen, back, sides, and glutes can reduce further and future injuries. By shifting the work of movement to the strong core muscles, the spine is protected from being overworked, which can improve pain.
1. Strengthen Surrounding Muscles
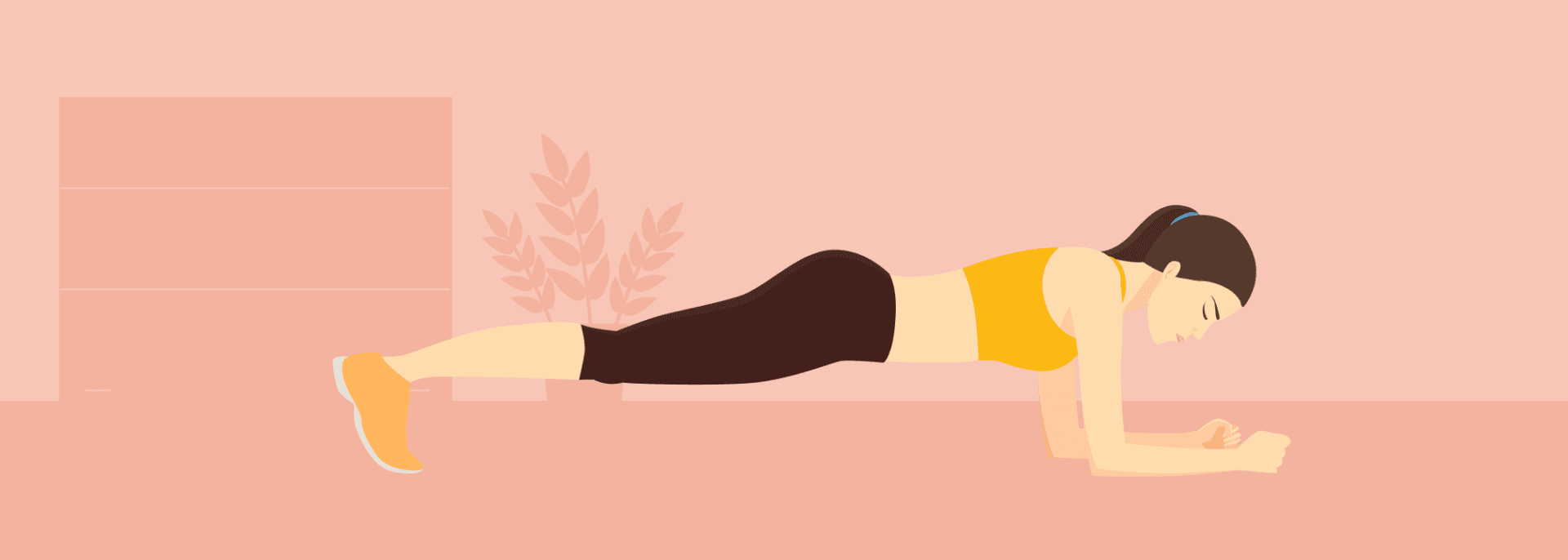
Planks:
Hold your body in a straight line, like a board, using your arms and toes for support. Your back should stay flat, your stomach muscles tight, and your body straight from your head to your feet. It’s great for strengthening your core, which includes your back, stomach, and hips.
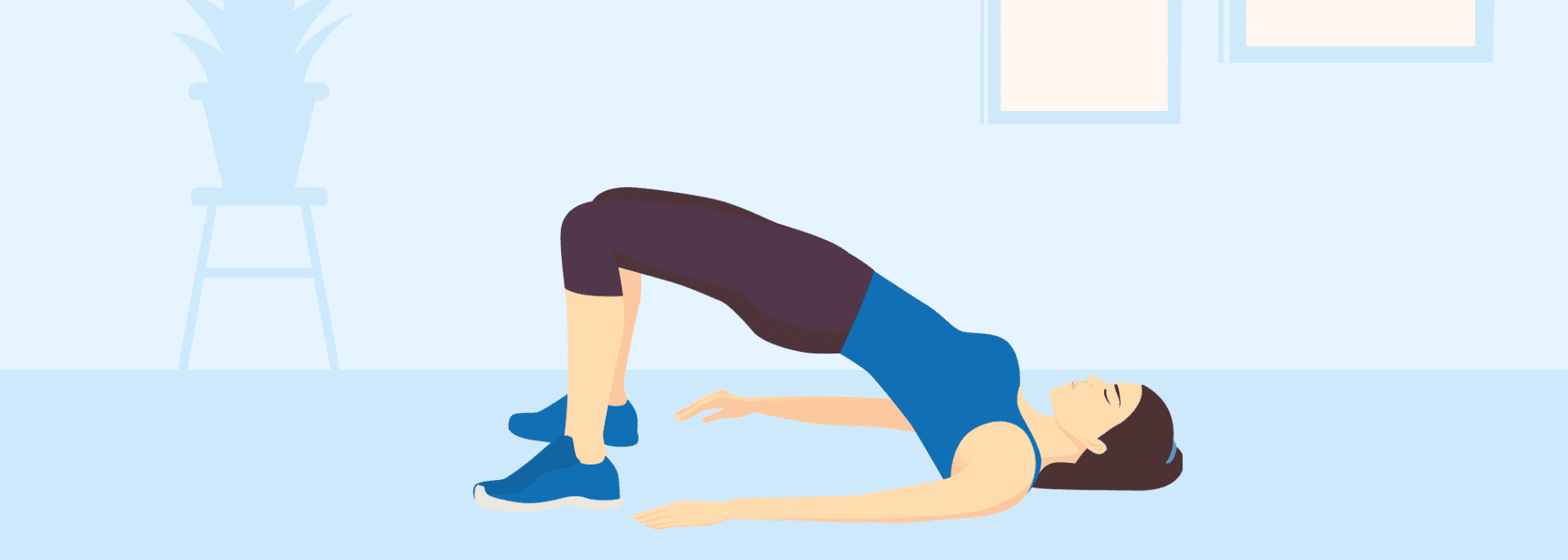
Bridges:
With your back flat on the ground, lift your hips to create a straight line from your knees to your shoulders, targeting your glutes and hamstrings while also engaging your core muscles, “bridging” your body between your feet and shoulder blades.
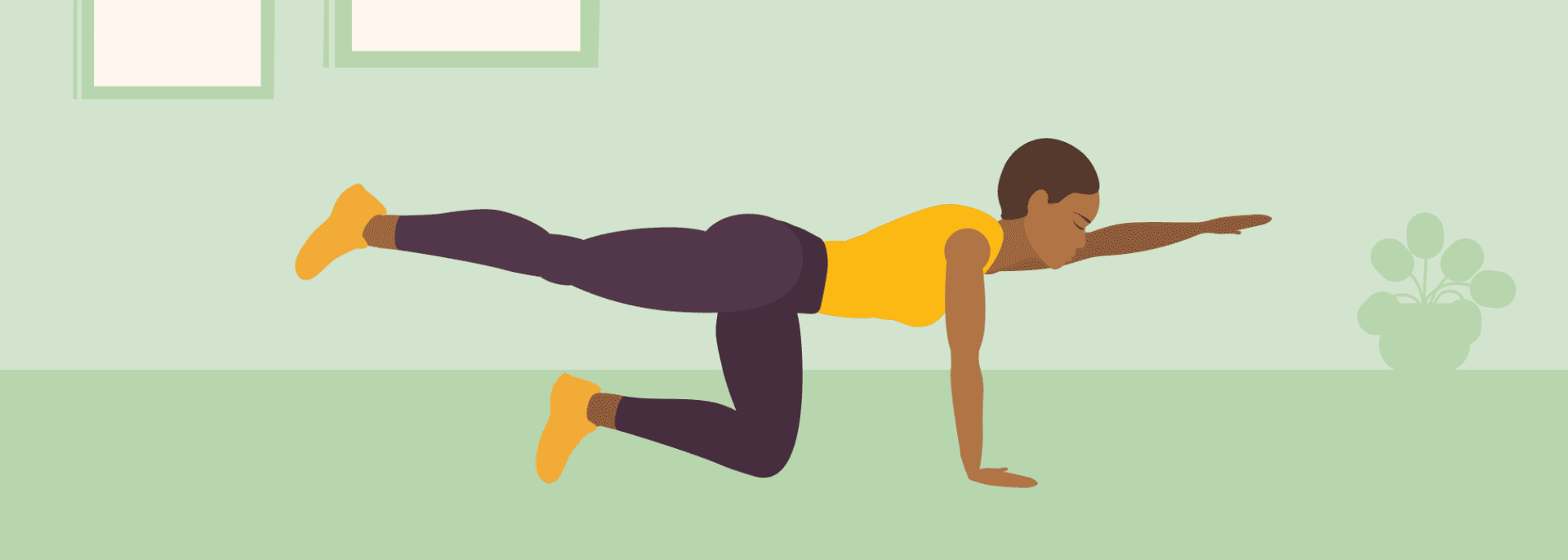
Bird Dogs:
Start on your hands and knees, then extend one arm straight out in front of you while also extending the opposite leg straight back behind you, maintaining a stable posture throughout the movement, mimicking the stance of a hunting dog “pointing” at prey. Alternate to the opposite side.

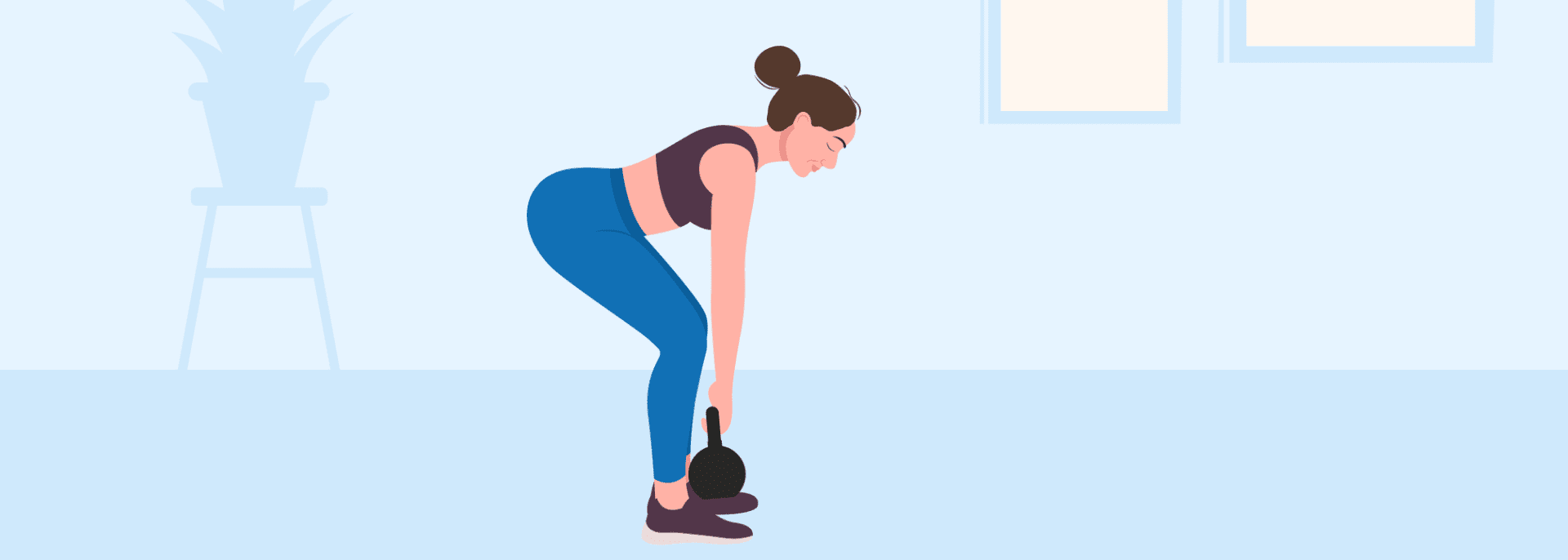
Deadlifts:
No-weight deadlifts are ideal for beginners to learn the movement, improve hip mobility, enhance posture, and strengthen without overloading. Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, hinge at the hips to allow your torso to lower until parallel with the ground, and let your arms hang in front of you to mimic holding an imaginary barbell. Use your core to stand back up and squeeze the glutes once you are upright, then repeat. Transition to weighted deadlifts as strength and form improve.

2. Improve Flexibility:
Maximizing the flexibility of the legs can protect the discs in the lower back. Every time you need that extra stretch, your flexible legs will give you what you need, rather than straining the discs of the spine as the default.
3. Practice Pain Management:
- Over-the-counter anti-inflammatories (e.g., ibuprofen) can decrease pain and reduce inflammation.
- Acetaminophen is a pain reliever that can alternate with anti-inflammatory agents to maximize relief.
- Additionally, using heat or ice therapy can relieve pain by reducing inflammation or relaxing muscles.
4. Engage in Low-Impact Exercise:
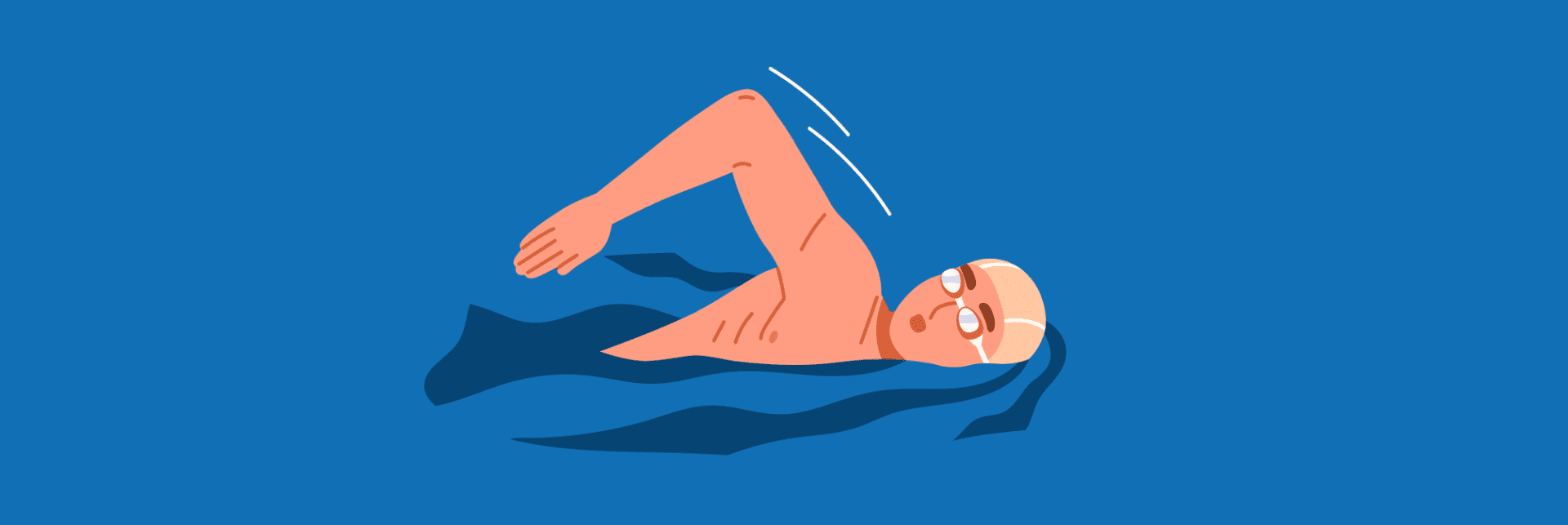

Maintaining flexibility in the legs, particularly the hamstrings, can help protect the lower back. Doing activities like swimming, walking, and yoga can strengthen muscles without placing excessive pressure on the spine.
5. Explore Traction and Inversion Therapies:
- Traction: A physical therapy technique to release the pressure of compressed discs can reduce pain.
- Inversion: An inversion table uses gravity to decompress the spine.
Degenerative Disc Disease Treatment Options:
When seeking treatment for neck or back pain caused by DDD, a variety of non-surgical options are available for patients. The goal of treatment is to improve symptoms and to be able to participate in desired life activities. Once this goal is reached, it is important to continue with a maintenance program to reduce the risk of recurrence. If this goal is not achieved, then surgical options are also available.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
First-line treatments: Several simple options can help alleviate immediate symptoms:
- Rest: Avoid activities that worsen the pain.
- Medications: Over-the-counter anti-inflammatories and pain relievers can help reduce discomfort and make daily activities more manageable.
- Physical therapy: Manual manipulation and guided exercises to strengthen weak muscles and improve flexibility. Trigger point needling can relax muscle spasms.
- Injections: Steroid injections to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Chiropractic care: Manual adjustments to improve spine alignment and motion.
- Acupuncture: Targets the mind-body connection and reduces pain.
Regenerative medicine treatments:
Regenerative medicine therapies can be life-altering as these targeted therapies stimulate the body’s natural healing process to repair damaged tissue, such as degenerative discs.
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP): A concentration of the platelets mixed with growth factors found in a patient’s blood. This therapy repairs damaged tissues.
- Bone marrow aspirate concentrate (BMAC): A concentration of a patient’s extracted bone marrow that contains the growth factors and mesenchymal stem cells that are stored there. This therapy repairs damaged tissues and promotes the growth of new tissues.
Surgical Treatment Options
These common surgical treatment options restore mobility and improve quality of life when non-operative treatments fail.
- Fusion: Removing the damaged disc and permanently connecting two or more vertebrae to eliminate movement and pain.
- Artificial Disc Replacement (arthroplasty): Removing and replacing the damaged disc with an artificial disc to preserve movement in the spine while eliminating pain. Ideal candidates are those with degenerative disc disease causing chronic pain in the neck (cervical spine) or lower back (lumbar spine).
Preventative Care
The best way to manage DDD is to focus on prevention. Early diagnosis of DDD from a spine specialist is the best way to understand the problem and develop a program to prevent symptoms, the development of further issues, and the need for formal treatments. Many people believe that seeing a spine surgeon will lead to having spine surgery, but the truth is that getting to the bottom of the problem early is the best way to avoid spine surgery altogether. Maintaining proper posture, engaging in regular exercise that targets the right areas, and preserving spine mobility can help slow down the degenerative process and prevent symptoms. By being proactive about spinal health early on, you can maintain flexibility and reduce the likelihood of developing severe or chronic symptoms in the future.
Conclusion
Degenerative Disc Disease is often misunderstood, but it’s actually far less intimidating: DDD is a natural part of aging much like skin wrinkling. While the term “disease” might sound alarming, disc degeneration happens to everyone over time – and it doesn’t automatically cause pain or a reduced quality of life. By understanding how the health of the discs changes over time and what symptoms to look for, you can manage DDD effectively with lifestyle adjustments and support. Having symptomatic DDD is not a life sentence. You can improve mobility, reduce discomfort and continue to live an active life with proper maintenance. Support your spine by seeking guidance from spine experts early and maintain proper spine care for a healthier, pain-free future.