Spine Glossary: Definitions & Phonetic Pronunciations

PARTS OF THE SPINE
Annulus Fibrosus
[AN-yuh-lus Fy-BROH-sus]
The tough, fibrous outer layer of an intervertebral disc, responsible for holding the disc together.
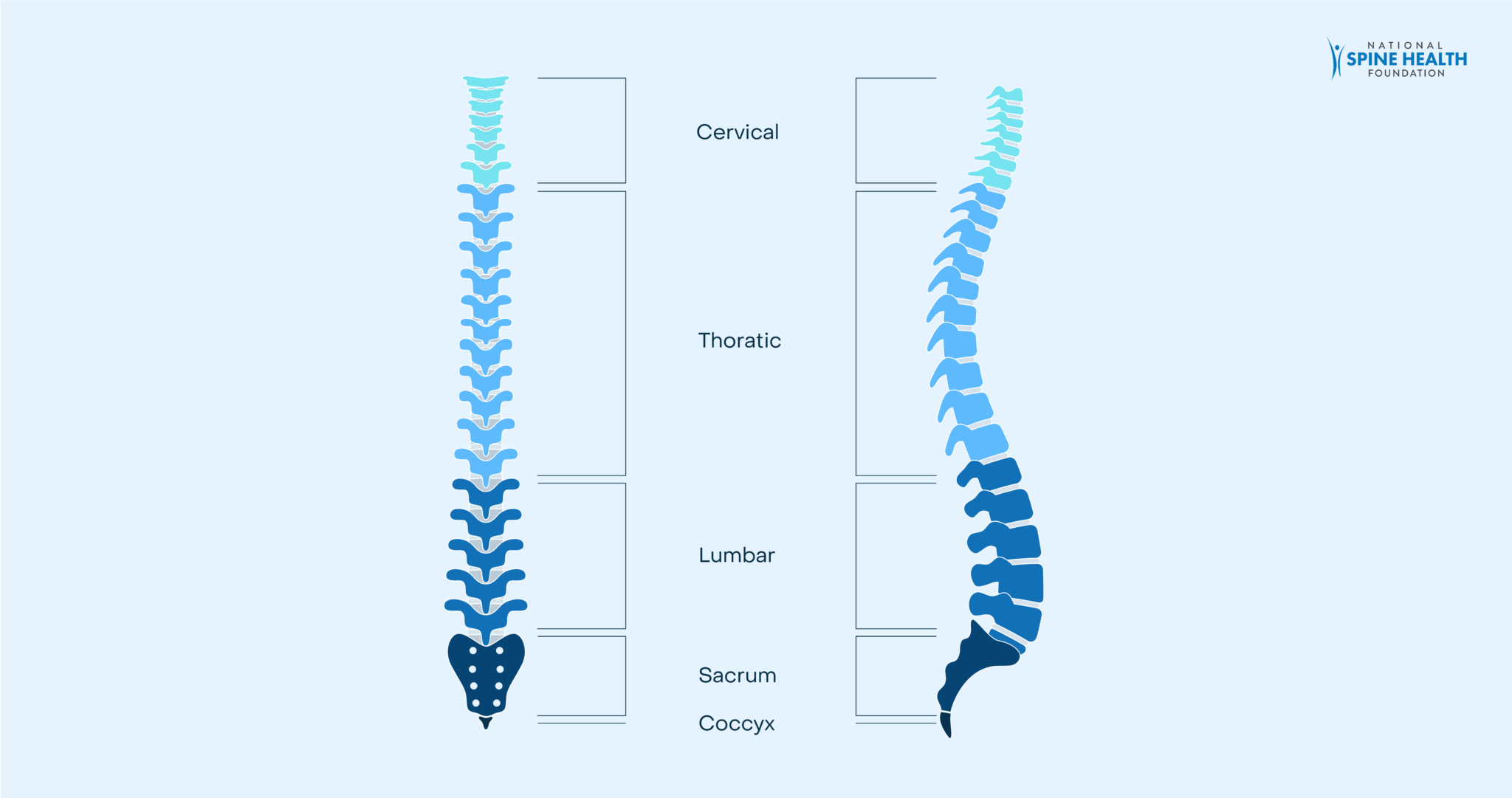
Cervical Curve
[SIR-vih-kul Curve]
The natural curve of the cervical spine, which is concave (curving inward) when viewed from the side.
Cervical Vertebrae
[SIR-vih-kul VUR-tuh-bray]
The seven vertebrae in the neck region (C1 to C7) that support the head and neck.
Coccyx
[KOK-siks]
Also known as the tailbone, it is a small, triangular bone located at the very end of the spine.
Costovertebral Joints
[KOS-toh-ver-TEE-bruhl Joints]
The joints where the ribs articulate with the thoracic vertebrae.
Dorsal (Posterior) Aspect
[DOR-suhl Pohs-TEER-ee-or AS-pekt]
The back side of the vertebral column.
Facet Joints
[FAS-it Joints]
Small, paired joints located on the back of adjacent vertebrae that enable spinal movement and stability.
Foramen Magnum
[foh-RAY-men MAG-num]
The large opening at the base of the skull through which the spinal cord exits the cranial cavity.
Inferior Articular Process
[in-FEER-ee-or ar-TIK-yoo-lar Process]
The part of the vertebra that articulates with the vertebra below it, forming another facet joint.
Intervertebral Discs
[IN-ter-ver-TEE-bruhl Discs]
The soft, cushion-like structures found between each pair of vertebrae, consisting of a tough outer layer (annulus fibrosus) and a gel-like inner core (nucleus pulposus).
Lamina
[LAM-ih-nuh]
The flat, thin part of the vertebral arch that connects the spinous process to the transverse process.
Lumbar Curve
[LUM-bar Curve]
The natural curve of the lumbar spine, which is concave (curving inward) when viewed from the side.
Lumbar Vertebrae
[LUM-bar VUR-tuh-bray]
The five largest vertebrae in the lower back (L1 to L5) responsible for bearing most of the body's weight and providing flexibility.
Nerve Root
The point at which a spinal nerve exits the spinal cord and travels to various parts of the body. Compression or irritation of nerve roots can lead to pain and dysfunction.
Nucleus Pulposus
[NOO-klee-us pul-POH-sus]
The gel-like center of an intervertebral disc, providing cushioning and shock absorption
Pedicle
[PED-i-kul]
The short, thick bony structure that connects the vertebral body to the posterior elements of the vertebra.
Sacroiliac Joint
[sak-roh-IL-ee-ak]
The joint connecting the sacrum to the pelvic bones, providing stability and support for the lower back.
Sacrum
[SAY-krum]
A triangular bone formed by the fusion of five sacral vertebrae, located at the base of the spine.
Spinal Column
The series of vertebrae that make up the backbone, including the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal regions.
Spinal Cord
A bundle of nerves that runs through the vertebral column, transmitting signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
Spinal Nerve Roots
The nerves that exit the spinal cord through small openings between vertebrae and travel to various parts of the body.
Spinous Process
[SPY-nus Process]
The bony projection at the back of each vertebra, which can be felt as the "ridge" along the spine.
Superior Articular Process
[soo-PEER-ee-or ar-TIK-yoo-lar Process]
The part of the vertebra that articulates with the vertebra above it, forming a facet joint.
Thoracic Curve
[thuh-RAS-ik Curve
The natural curve of the thoracic spine, which is convex (curving outward) when viewed from the side.
Thoracic Vertebrae
[thuh-RAS-ik VUR-tuh-bray]
The twelve vertebrae in the upper and mid-back region (T1 to T12) that connect to the ribs and protect the vital organs.
Transverse Process
[TRANZ-vurs Process]
The bony projections on each side of a vertebra that provide attachment points for muscles and ligaments.
Ventral (Anterior) Aspect
[VEN-tral an-TEER-ee-or AS-pekt]
The front or belly side of the vertebral column.
Vertebra
[VUR-tuh-bruh]
One of the individual bones that make up the spine. There are 33 vertebrae in total.
Vertebral Foramen
[VUR-tuh-bruhl fuh-RAY-muhn]
The central opening in each vertebra through which the spinal cord passes.
Zygapophysial Joints (Facet Joints)
[zye-guh-poh-FIZH-ee-ul Joints]
The joints formed by the articulation of the superior and inferior articular processes of adjacent vertebrae.
SPINE AND RELATED CONDITIONS

Cauda Equina Syndrome
[KAW-duh ee-KWY-nuh SIN-drohm]
A rare but serious condition where nerves at the base of the spinal cord are compressed, leading to loss of bowel and bladder control.
Degenerative Disc Disease
[dih-JEN-er-uh-tiv Disc Disease]
The gradual breakdown of the discs between the vertebrae, often associated with aging and leading to pain and reduced mobility.
Herniated Disc
[HUR-nee-ay-ted Disc]
When the soft inner core of a disc pushes through the tough outer layer, often causing pain and discomfort.
Hyperkyphosis
[HAHY-per-ki-FOH-sis]
An excessive outward curvature of the thoracic spine, causing a hunched or rounded back.
Hyperlordosis
[HAHY-per-lor-DOH-sis]
An excessive inward curvature of the lumbar spine, causing the lower back to arch excessively.
Myelopathy
[mahy-uh-LAH-puh-thee]
A disorder of the spinal cord, often caused by compression or injury, resulting in symptoms such as weakness, numbness, and coordination problems.
Osteoporosis
[OS-tee-oh-puh-ROH-sis]
A condition characterized by weakened bones, increasing the risk of vertebral compression fractures.
Radiculopathy
[RAD-ih-kyoo-LAH-puh-thee]
A condition in which a nerve root is irritated or compressed, leading to pain, weakness, and numbness along the path of the affected nerve.
Sciatica
[sahy-AT-i-kuh]
A condition characterized by pain, tingling, or numbness that radiates along the path of the sciatic nerve, often caused by compression or irritation of the nerve roots in the lumbar spine.
Scoliosis
[skoh-lee-OH-sis]
A condition characterized by an abnormal curvature of the spine, often in an "S" or "C" shape.
Spinal Stenosis
[Spinal stuh-NOH-sis]
A narrowing of the spaces within the spine, which can put pressure on the spinal cord and nerves, leading to pain and weakness.
Spondylolisthesis
[spon-dih-loh-lis-THEE-sis]
A condition where one vertebra slips forward or backward in relation to the one below it, potentially compressing nerves and causing pain.
Vertebral Compression Fracture
[VUR-tuh-bruhl Compression Fracture]
A break or fracture in one or more vertebrae, often caused by osteoporosis or trauma.
MEDICAL CARE AND DIAGNOSTICS

Chiropractor
A healthcare professional specializing in the diagnosis and treatment of musculoskeletal disorders, often focusing on spinal adjustments and alignment.
CT Scan (Computed Tomography)
[kuhm-PYOO-ted tuh-MOG-ruh-fee]
A medical imaging technique used to create detailed cross-sectional images of the spine and surrounding structures.
DXA Scan (Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry)
[Dual-energy X-ray ab-sorp-tee-AW-muh-tree]
A medical imaging technique used to measure bone density and diagnose conditions like osteoporosis by assessing the mineral content of bones.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
[mag-NEH-tik REZ-uh-nuhns Imaging]
A diagnostic imaging technique used to visualize the structures of the spine, including the discs, nerves, and vertebrae.
Myelogram
[mahy-uh-loh-gram]
An X-ray procedure where a contrast dye is injected into the spinal canal to visualize the spinal cord and nerves.
Neurosurgeon
[NOOR-oh-SUR-jun]
A surgeon specializing in the surgical treatment of disorders of the nervous system, including spine conditions.
Orthopedic Surgeon
A medical doctor specializing in the diagnosis and treatment of musculoskeletal conditions, including spine-related issues.
Pain Management Physician
A physician who focuses on diagnosing, treating, and managing various types of pain, using a multidisciplinary approach to improve patients' quality of life.
Pain Management Psychiatrist
A medical professional who specializes in addressing the psychological and emotional aspects of chronic pain, helping patients cope with pain-related distress and improve their overall well-being.
Physical Therapist
A healthcare professional trained to assess and treat physical impairments, disabilities, and injuries through various therapeutic exercises and techniques to improve mobility and function.
X-ray
A common imaging method used to capture images of the bones in the spine, helping to identify fractures and deformities.
TREATMENTS: SURGICAL AND NONSURGICAL

Disc Arthroplasty
[Disc AHR-throh-plas-tee]
A surgical procedure involving the removal of a damaged or degenerated intervertebral disc in the spine and its replacement with an artificial disc implant to alleviate pain and improve spinal mobility. Also known as artificial disc replacement or spinal disc replacement.
Discectomy
[dih-SEK-tuh-mee]
A surgical procedure to remove all or part of a herniated disc to alleviate pressure on nerves.
Epidural Steroid Injection
[EP-uh-DOO-ruhl STER-oid Injection]
A procedure where anti-inflammatory medication is injected into the epidural space of the spine to reduce pain and inflammation.
Facet Joint Injection
[FAS-it Joint Injection]
An injection into the facet joints to relieve pain and diagnose the source of back or neck pain.
Fusion Surgery
A surgical procedure that joins two or more vertebrae together to stabilize the spine, often used to treat conditions like spondylolisthesis and spinal fractures.
Kyphoplasty
[kahy-FOH-plas-tee]
A procedure similar to vertebroplasty that involves inflating a balloon in the fractured vertebra before injecting cement.
Laminectomy
[LAM-uh-NEK-tuh-mee]
A surgical procedure to remove a portion of the vertebra called the lamina to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves.
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Surgical procedures that use small incisions and specialized instruments to treat spine conditions, often resulting in faster recovery times.
Nerve Block
A medical procedure in which an anesthetic or medication is injected directly into a specific nerve or nerve group to temporarily block pain signals and provide relief from pain or discomfort in a particular area of the body.
Orthosis
[or-thow-suhs]
A brace used to support and immobilize the spine, often prescribed for scoliosis or after spine surgery.
Regenerative Medicine
A multidisciplinary field of medical research and treatment using techniques such as stem cell therapy, tissue engineering, and growth factors to repair or replace damaged or degenerated tissues and organs.
Rehab
Rehabilitation typically involving a structured program of physical therapy and exercises designed to improve spinal function, strengthen supporting muscles, and reduce pain and disability.
Vertebroplasty
[VUR-tuh-broh-plas-tee]
A minimally invasive procedure where a special cement is injected into a fractured vertebra to stabilize it.